Spasticity is a prevalent and frequently disabling motor disorder in children with cerebral palsy.1 Cerebral palsy is the most common motor disability in childhood, leading to lifelong physical disability.2,3

Spasticity in children
Unilateral and bilateral cerebral palsy
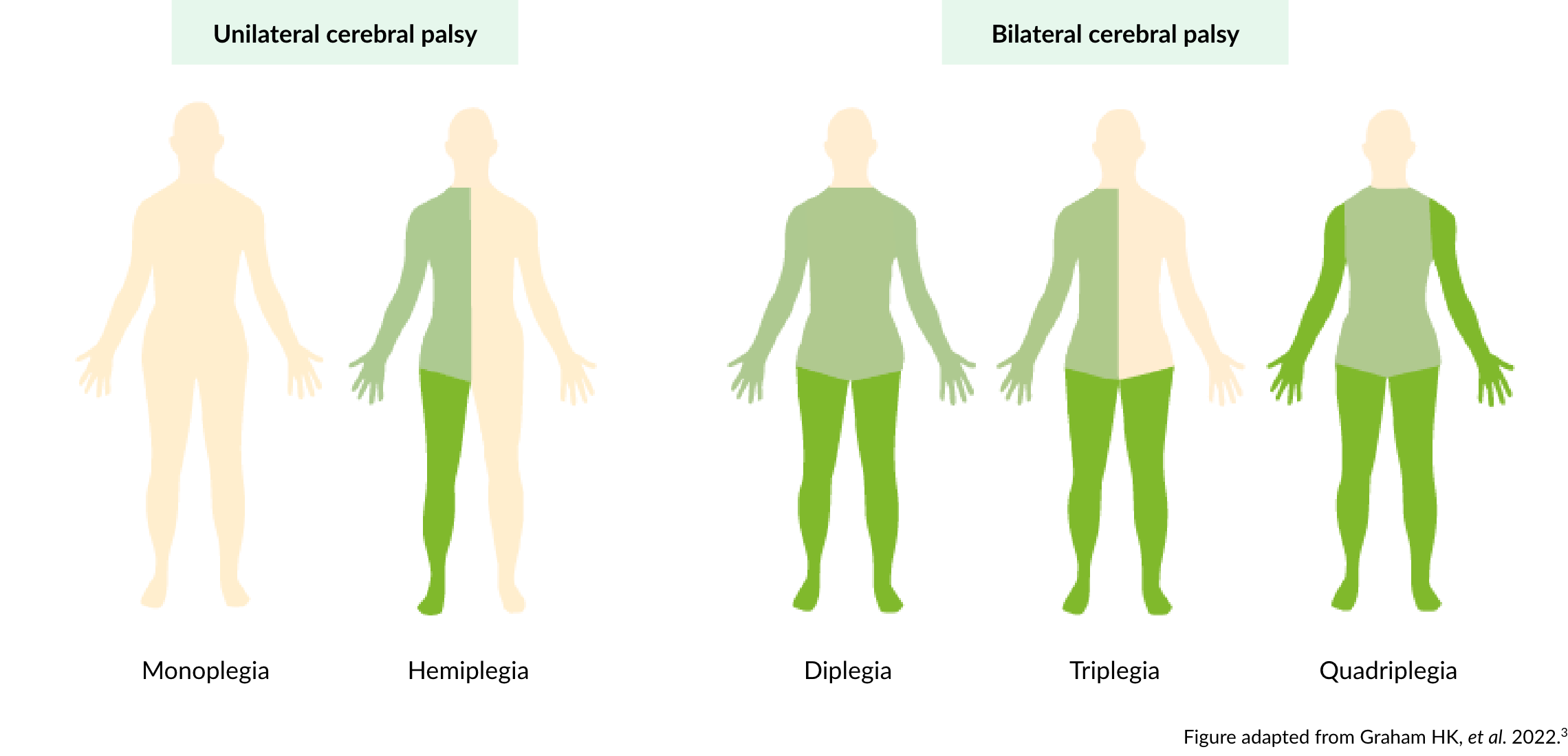
In monoplegia, the one limb affected is more often the lower limb.3 In hemiplegia, one side of the body is affected, and the upper limb is usually more involved than the lower limb.3 In diplegia, all limbs are affected, but the lower limbs are much more affected than the upper limbs.3 Triplegia usually has unilateral upper limb and bilateral (asymmetrical) lower limb involvement. In quadriplegia, the whole body is involved.3
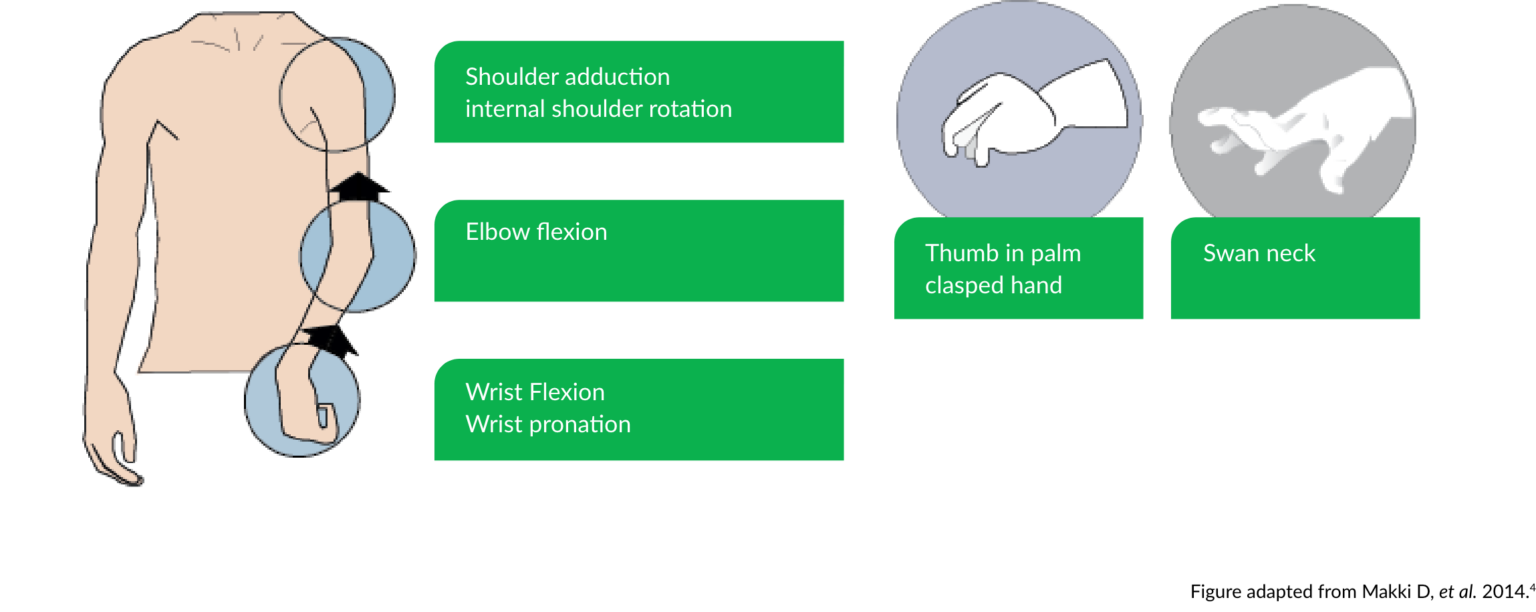
More than 80% of children with cerebral palsy have upper limb involvement.4 Spasticity of the upper limbs affect the ability to perfom activities of daily living, such as eating, drinking, grooming and dressing.5
Common patterns of upper limb spasticity in children4
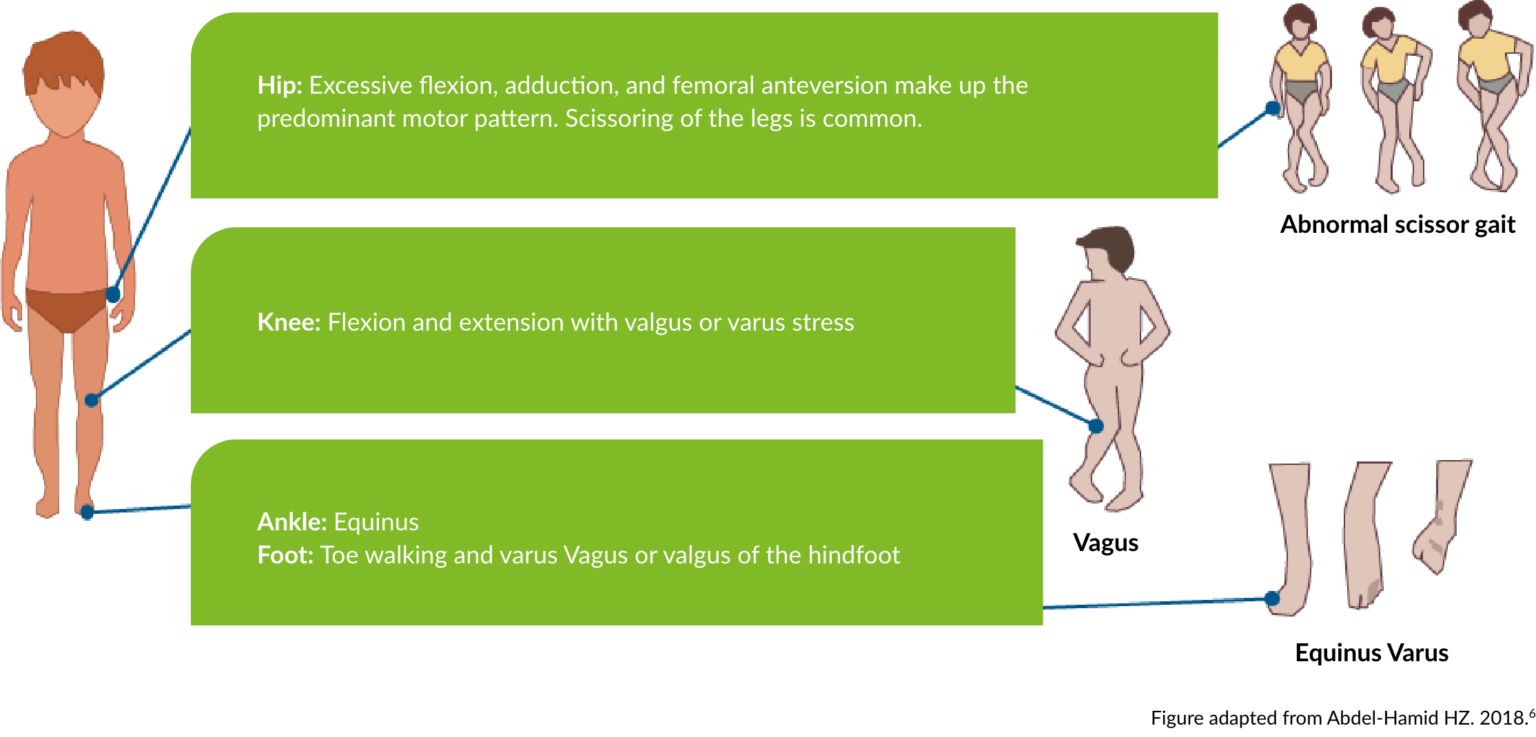
Lower limb involvement leads to a tendency for the hips to be flexed and adducted with the knees flexed and in valgus, and the ankles in equinus, resulting in toe walking.6
Common patterns of lower limb spasticity in children6
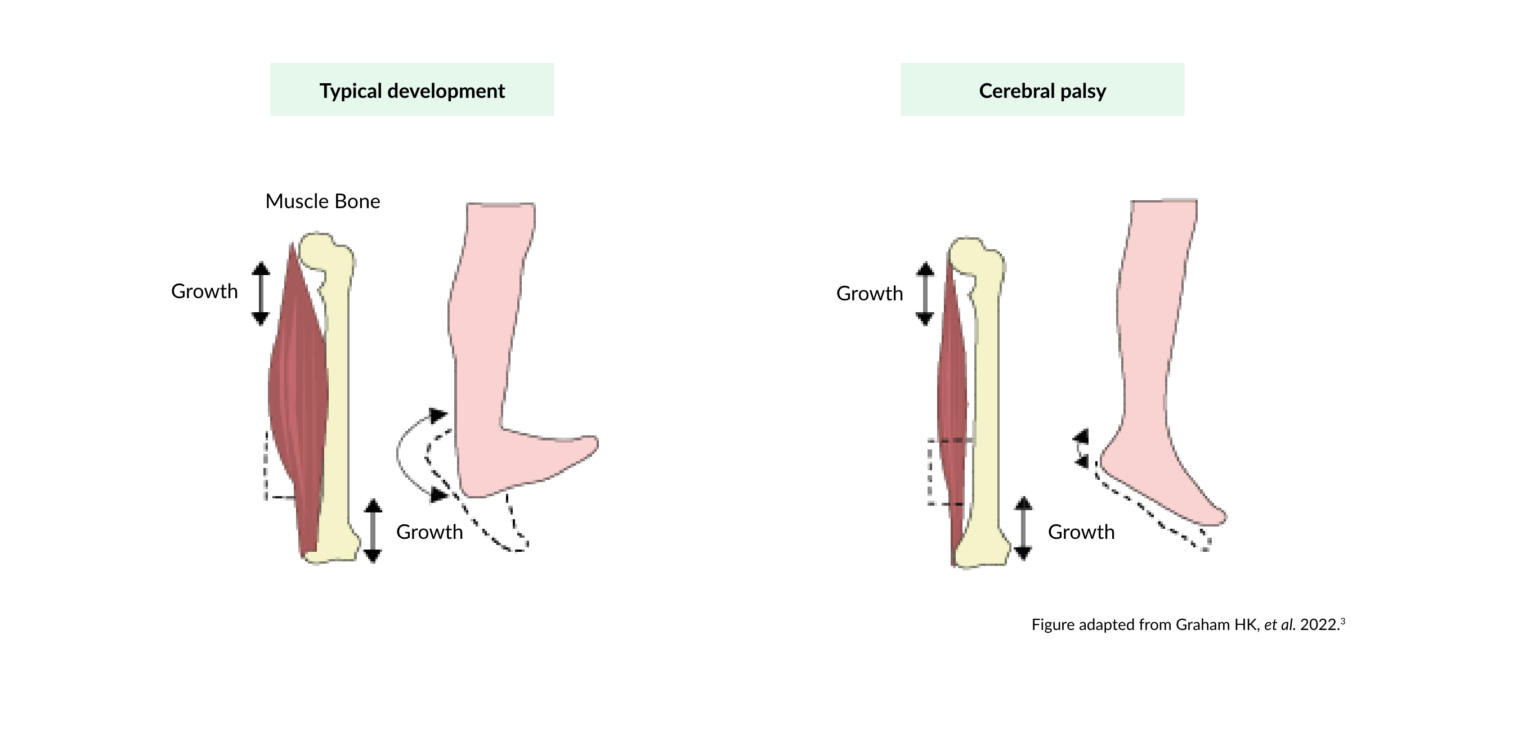
Over time, fixed contractures develop that increase disability.7
Children with cerebral palsy have long sarcomere lengths compared with those observed during typical child development3
Spasticity of the lower limbs results in deformity that can affect ambulation, bed positioning, sitting, chair level activities, transfers and standing up.11
When used in conjunction with occupational therapy, Dysport® can reduce muscle spasticity and optimise the effects of therapies used for enhancing motor ability and improving functional skills.12,13
References:
- Tilton A, et al. J Child Neurol. 2017;32(5):482–487.
- Centre of Disease Control and Prevention. What is Cerebral Palsy? Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/cp/facts.html (Accessed: September 2025).
- Graham HK, et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:15082.
- Makki D, et al. J Child Orthop. 2014;8(3):215–219.
- Arnould C, et al. Front Neurol. 2014;4;5:48.
- Abdel-Hamid HZ. Cerebral Palsy Clinical Presentation. Available at: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1179555-clinical#b3 (Accessed: September 2025).
- Skalsky AJ and MacDonald CM. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2012;23:675–687.
- Pandey K. Spasticity Clinical Presentation. Available at: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2207448-clinical (Accessed: September 2025).
- Hoare B, et al. BMC Neurol. 2010;10:58.
- Lidman GRM, et al. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2020;62(2):252–258.
For further information, please refer to the Prescribing Information or the Summary of Product Characteristics.

